Description
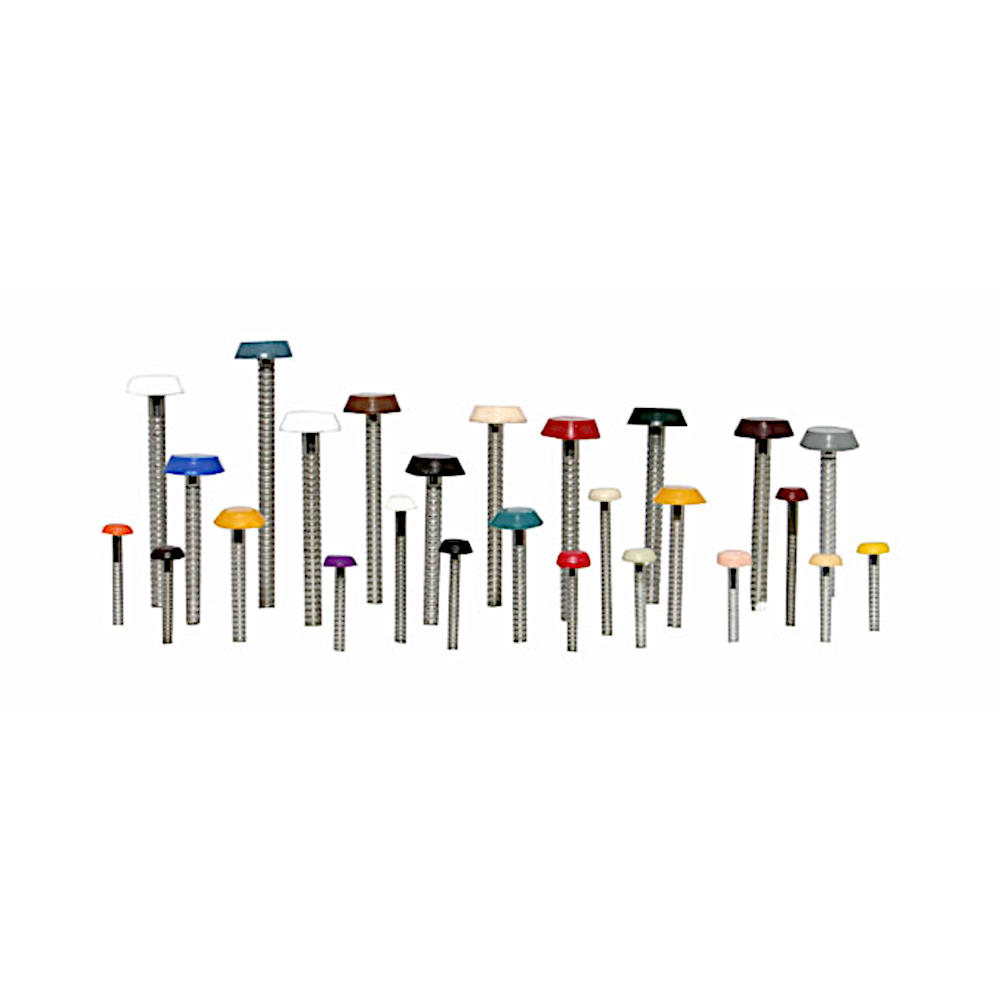
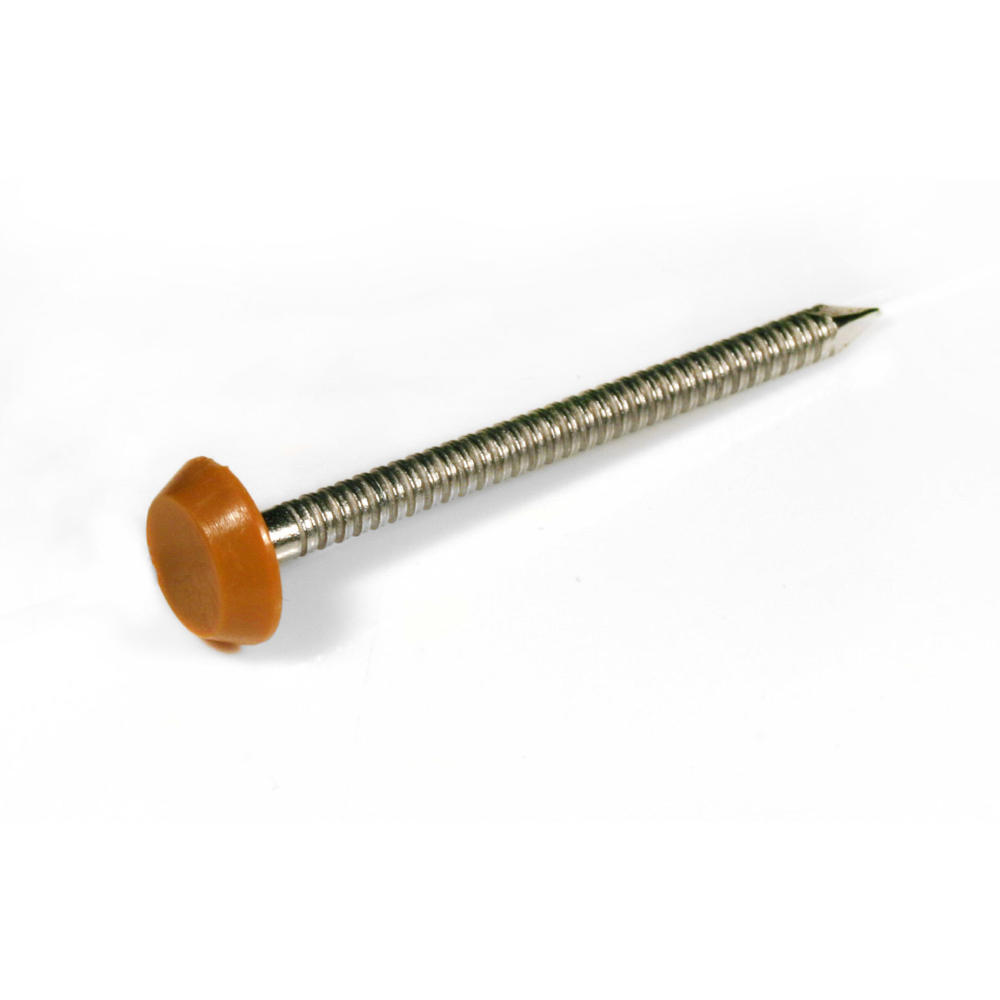
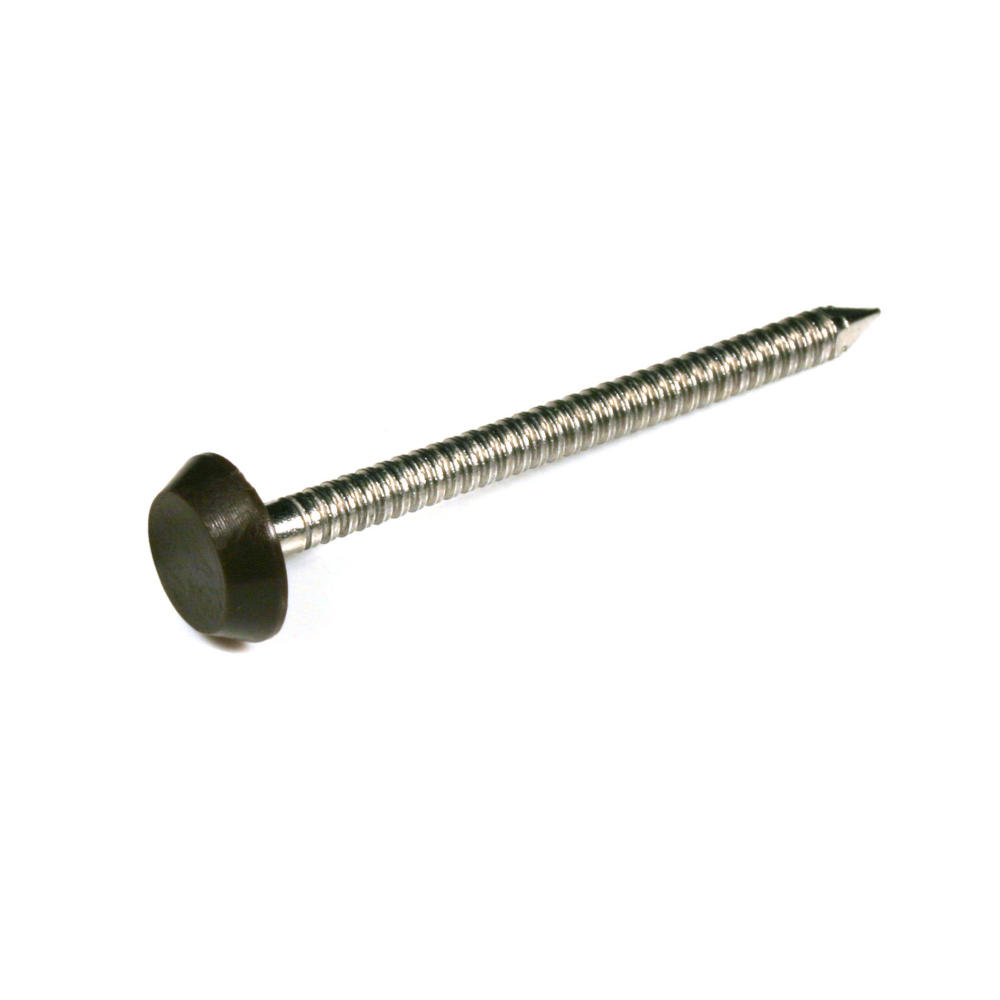
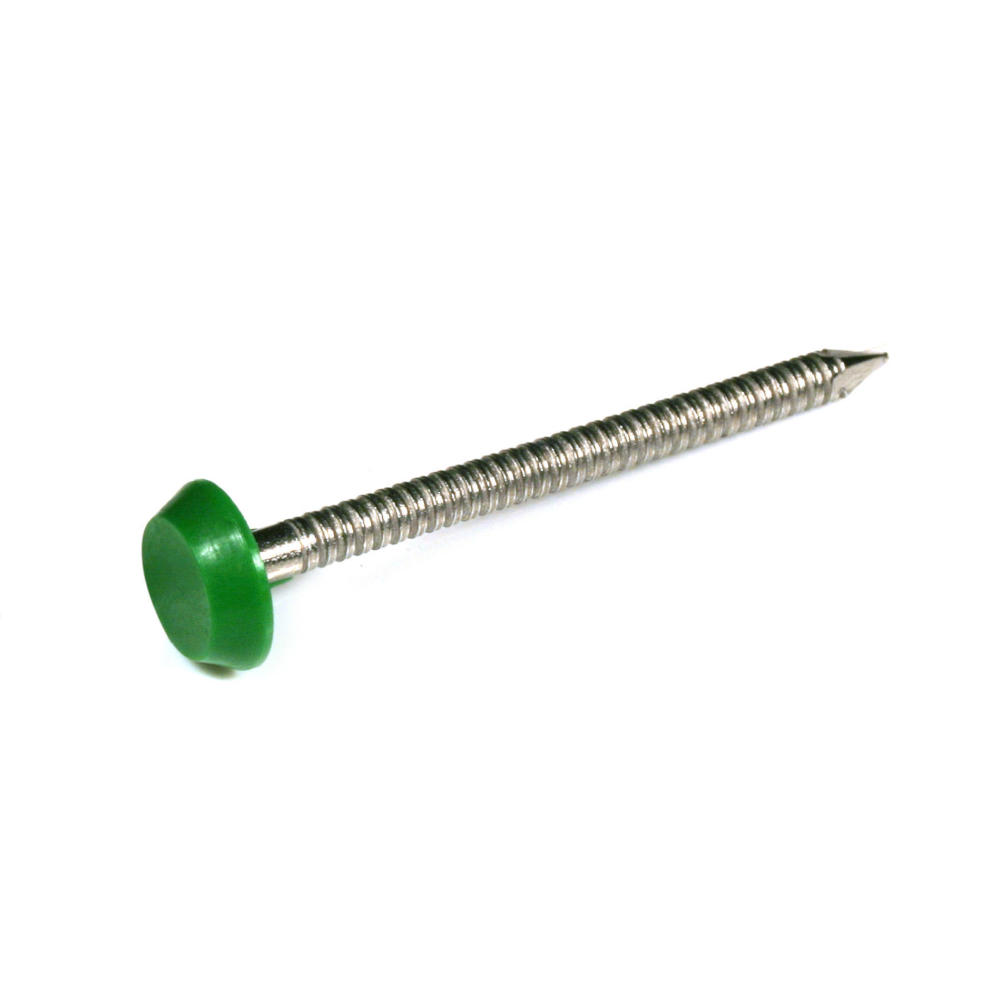
With securely moulded heads made from special tough polymer plastic, POLYTOPS® nails are shatter-resistant to hammer. Every batch is destructively tested to failure on a drop test rig to simulate the product in use on-site. A level is set when remedial action must be taken to restore quality.
Their specially designed tapered, annular ring shank provides better gripping characteristics than ordinary smooth nails enabling a stronger holding power and tamper resistance. Poor ring shank can result in less secure installation. We ensure POLYTOPS® polymer-head nails offer you a secure fixing by testing the pull out force required and therefore their security. These independent tests were carried out at Loughborough University Department of Engineering. POLYTOPS® nails have been accredited with the CE mark in June 2015.
POLYTOPS® Polymer-Headed Nails
Available in different sizes and a wide range of colours, POLYTOPS® nails can be used on a variety of construction and building applications inside and out. They come in POLYTOPS® branded boxes of 100 pcs.
They are used for fastenings:
- Fascia & soffits
- Barge boards
- Cladding
- Window & door trims
- Panelling
- Skirting, architrave & decking
- Pins vs Nails
Generally, our plastic-topped pins are used for fastening soffits. Whereas, the plastic topped nails are used on the fascia. This is due to soffits being thinner boards to the fascia so only require 30mm or 40mm pins. Fascia tend to be thicker and require our more heavy-duty 50mm or 65mm nails. This is only a general guide. It will ultimately be determined by the thickness of the board that requires fastening and what is being fastened to.
POLYTOPS® Polymer Headed Nails Technical Specification
POLYTOPS® Nails are CE-approved for the intended use with construction products, in accordance with the applicable harmonised technical specification, such as PVC Fascia, Barge Board, Cladding or Trim Fixing.
Under tests, A4 stainless steel has been shown to withstand a saltwater environment and not experience any corrosion. Under the same tests A2 stainless steel was subject to heavy corrosion which can lead to damage to the surrounding area.